Know Abour 4C's
Colour
Diamonds come naturally in every color of the rainbow. However most people are concerned with diamonds in the white range. The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) rates the body color in white diamonds from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow). The differences from one grade to the other are very subtle and it takes a trained eye and years of experience to color grade a diamond.
Clarity
The clarity of a diamond is determined by the amount and location of flaws, or blemishes, in the diamond when viewed under 10 power (10x) magnification. GIA rates clarity grades in diamonds from Flawless to Imperfect 3 (see chart below). The Diamond Shopping Network offers you diamonds from the Imperfect 1 grade through Flawless.
Cut
When we speak of cut we are more interested in the proportions of the diamond as opposed to its shape (Round Brilliant, Marquise, Pear, Princess, etc.) Every diamond regardless of its shape gets it brilliancy and scintillation by cutting and polishing the diamond facets to allow the maximum amount of light that enters through its top to be reflected and dispersed back through its top.
Carat Weight
Carat is the unit of weight for all gemstones. One carat is subdivided into 100 "points". Therefore a diamond measuring 75 points is 3/4 carat in weight, or 0.75ct. There are five carats in a gram. The word "carat" comes from the seed of the carob tree pod which is found in tropical climates. These seeds were used until this century to weigh precious gems.
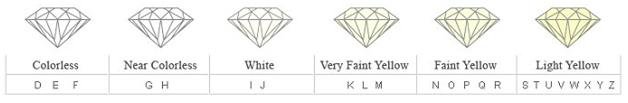
Colour
Color refers to a diamond's lack of color, grading the whiteness of a diamond.
A color grade of D is the highest possible, while Z is the lowest.
A diamond's color grade is based on its lack of color. The less color a diamond has, the higher its color grade. After cut, color is generally considered the second most important characteristic when selecting a diamond. This is because the human eye tends to detect a diamond's sparkle first, and color second. Diamonds graded J or better are colorless or near-colorless.
D - Absolutely colorless The highes color grade. Extremely rare
E,F - Colorles. Minute traces of color can be detected by an expert gemologist.
G,H - Near colorless. Color difficult to detect unless compared side-by-side against diamonds of better grades.
I,J - Near colorless. An exceptional value with slightly detectable warmth or tone
K,L,M - Noticeable color
N to Z - Easily Noticeable color

Carat Weight
Carat is specifically a measure of a diamond's weight A one-carat diamond is comprised of 100 points called cents . Hence, 50 cents is equal to 1/2-carat, and so on.
Most of the time ,value of the diamond increases with increase in Carat size.
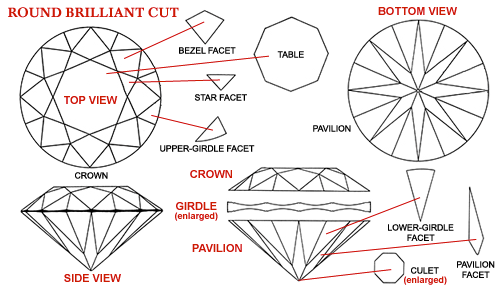
Cut
Cut is a diamond's most important characteristic. It has the greatest overall influence on a diamond's beauty. It determines what we generally think of as sparkle.
A diamond's cut grade is an objective measure of a diamond's light performance, or, what we generally think of as sparkle. When a diamond is cut with the proper proportions, light is reflected back to the top of the diamond. If it is cut too shallow, light leaks out of the bottom; too deep and it escapes out of the side.
EX - Excellent: Reflects nearly all light that enters the diamond. An exquisite and rare cut. All the dimensions are perfectly maintained in the described mathematical proportions in order to get the most sparkle.
VG - Very good cut: Reflects almost the same light as an Excellent cut, with slightly broader proportions.
GD - Good cut: Reflects most light that enters. In this case , cutter might have chosen to get bigger size to make it more economical.
FR - Fair cut: Reflects lower proportion of light due to weaker proportion that cutter has chosen to get maximum size or yield . These cuts are heavily discounted in price.
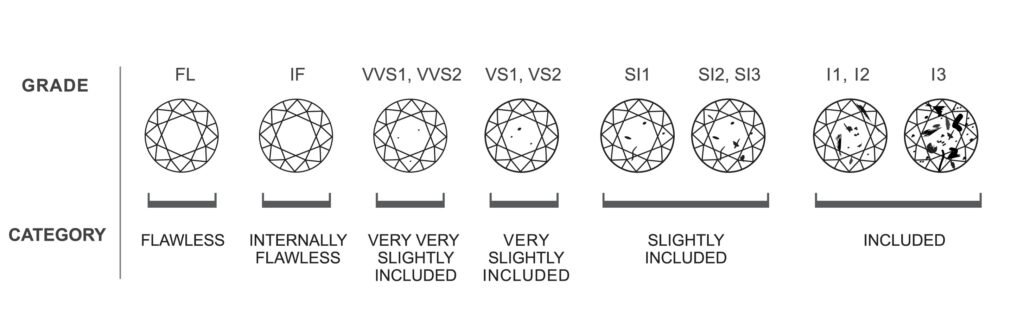
Clarity
Clarity is a measure of the number and size of the tinyimperfections that occur in almost all diamonds.
Many of these imperfections are microscopic, and do notaffect a diamonds beauty in any discernible way.
Clarity simply refers to the tiny, natural imperfectionsthat occur in all but the finest diamonds. Gemologists refer to theseimperfections by a variety of technical names, including blemishes andinclusions, among others.
Diamonds with the least and smallest imperfectionsreceive the highest clarity grades. Because these imperfections tend to bemicroscopic, they do not generally affect a diamonds beauty in any discernibleway.
"eye-clean" diamond is the one that has noimperfections visible to the unaided-eye through the face-up.
FL,IF - Flawless, Internally Flawless: No internal or external imperfections. Internally Flawless: No internal imperfections. Very rare.
VVS1,VVS2 - Very, Very Slightly Included: Very difficult to see imperfections under 10x magnification. An excellent quality diamond.
VS1,VS2 - Very Slightly Included: Imperfections are not typically visible to the unaided eye. Less expensive than the VVS1 or VVS2 grades.
SI1,SI2 - Slightly Included: Imperfections are visible under 10x magnification, and may be visible with the unaided eye.
I1 - Included: This grade of diamonds will have minor inclusions that may be visible to the unaided eye.
I2,I3 - Inclusions are heavy and visible to the unaided eye.
Know About Gemstone
Gemstones are naturally occurring, mineral crystals that are valued for their beauty, durability, and rarity, often used in jewelry. They are typically cut and polished to enhance their luster and color. Gemstones can be broadly classified as precious or semi-precious, with precious stones like diamonds, rubies, sapphires, and emeralds being highly valued for their rarity and exceptional qualities.
Here's a more detailed look:
What are Gemstones?
Definition:
A gemstone is a mineral crystal that is cut and polished to be used for jewelry or other adornments.
Origin:
Gemstones are naturally formed in the earth's crust, often through the cooling of mineral-rich hydrothermal water or as a result of rock transformations.
Categories:
Precious Stones: Diamonds, rubies, sapphires, and emeralds are the four traditionally recognized precious gemstones.
Semi-Precious Stones: This category includes a wide variety of gemstones, such as amethyst, garnet, opal, tourmaline, and many others.
Factors that Determine Gemstone Value:
Rarity: Gemstones that are less common are generally more valuable.
Beauty: A gemstone's color, clarity, and cut all contribute to its visual appeal and value.
Durability: The hardness and resistance of a gemstone to scratching and wear affect its suitability for jewelry and, consequently, its value.
Common Gemstones and Their Characteristics:
Diamond: Known for its hardness, brilliance, and clarity.
Ruby: A red gemstone, a variety of corundum, prized for its deep color.
Sapphire: A blue gemstone, also a variety of corundum, valued for its durability and color.
Emerald: A green gemstone, a variety of beryl, prized for its rich color and transparency.
Amethyst: A purple gemstone, a variety of quartz, known for its beauty and affordability.
Opal: Known for its unique play-of-color and water-like appearance.
Pearl: An organic gemstone, produced by mollusks, known for its smooth surface and pearly luster.

Yellow Sapphire - Pukhraj
Species: Corundum
Hardness: 9
Refractive Index (RI) : 1.762~1.770
Color: Light to Dark Yellow, Pale - Yellow,
Orangish Golden - Yellow
Occurrence: Sri Lanka, Burma, Thailand, Cambodia, Africa, Australia.

Blue Sapphire - Neelam
Species: Corundum
Hardness: 9
Refractive Index (RI) : 1.762~1.770
Color: Light to Dark Blue, Violetish - Blue, Greenish - Blue, Purplish - Blue
Occurrence: Kashmir, Burma, Thailand, Pakistan, Vietnam, Sri Lanka, Africa, Australia.

Ruby - Manaik
Species: Corundum
Hardness: 9
Refractive Index (RI): 1.762~1.770
Color: Light to Dark Red, pinkish/Purplish Red
Occurrence: Burma, Thailand, Pakistan, Vietnam, Sri Lanka, Africa.

Emerald - Panna
Species: Chrysoberyl
Hardness: 7.5-8
Refractive Index (RI): 1.577~1.583
Color: Light to Dark Green.
Occurrence: Colombia, Brazil, Russia, Zambia, India.

Pearl - Moti
Species: Fresh Water, Salt Water
Hardness: Varies
Refractive Index (RI): Not Applicable (Opaque)
Color: White, Grey, Yellowish - White, Light - Cream, Black, Body - Color
Occurrence: Seas of Basra, South Sea, Tahiti, Arabia, Australia, Japan, Bahrain, Persia.

Hessonite - Gomed
Species: Grossularite
Hardness: 7 - 7.5
Refractive Idex (RI): 1.740
Color: Brown, Brownish - Orange, Orangish - Brown.
Occurrence: Sri Lanka, Canada, Canada, Brazil. Africa, Madagascar.

Red Coral - Lal Moonga
Species: Corundum
Hardness: 3.5 - 4.0
Refractive Index (RI) : Not Applicable as they are Opaque
Color: Flesh Pink, Dark Blood Red, Orange, Orangish - Red, Brownish - Red
Occurrence: Mediterranean Sea, Red Sea, Sea near Spain, Morocco, Malaysia, Japan.

Diamond - Hira
Species: Carbon
Hardness: 10
Refractive Index (RI): 2.417
Color: Colorless, Yellow, Brown, Red, Green, blue, other Fancy Colors
Occurrence: Africa, Russia, Canada, Australia, India.

Cats Eye - Lahsuniya
Species: Chrysoberyl
Hardness: 8.5
Refractive Index (RI): 1.744~1.755
Color: Light to Dark Greenish - Yellow, Green, Brownish Green, Brownish - Yellow.
Occurrence: Sri Lanka, Brazil, Russia, Tanzania, China.
Know Abour 4C's
Colour
Diamonds come naturally in every color of the rainbow. However most people are concerned with diamonds in the white range. The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) rates the body color in white diamonds from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow). The differences from one grade to the other are very subtle and it takes a trained eye and years of experience to color grade a diamond.
Clarity
The clarity of a diamond is determined by the amount and location of flaws, or blemishes, in the diamond when viewed under 10 power (10x) magnification. GIA rates clarity grades in diamonds from Flawless to Imperfect 3 (see chart below). The Diamond Shopping Network offers you diamonds from the Imperfect 1 grade through Flawless.
Cut
When we speak of cut we are more interested in the proportions of the diamond as opposed to its shape (Round Brilliant, Marquise, Pear, Princess, etc.) Every diamond regardless of its shape gets it brilliancy and scintillation by cutting and polishing the diamond facets to allow the maximum amount of light that enters through its top to be reflected and dispersed back through its top.
Carat Weight
Carat is the unit of weight for all gemstones. One carat is subdivided into 100 "points". Therefore a diamond measuring 75 points is 3/4 carat in weight, or 0.75ct. There are five carats in a gram. The word "carat" comes from the seed of the carob tree pod which is found in tropical climates. These seeds were used until this century to weigh precious gems.
Colour
Color refers to a diamond's lack of color, grading the whiteness of a diamond.
A color grade of D is the highest possible, while Z is the lowest.
A diamond's color grade is based on its lack of color. The less color a diamond has, the higher its color grade. After cut, color is generally considered the second most important characteristic when selecting a diamond. This is because the human eye tends to detect a diamond's sparkle first, and color second. Diamonds graded J or better are colorless or near-colorless.
D - Absolutely colorless The highes color grade. Extremely rare
E,F - Colorles. Minute traces of color can be detected by an expert gemologist.
G,H - Near colorless. Color difficult to detect unless compared side-by-side against diamonds of better grades.
I,J - Near colorless. An exceptional value with slightly detectable warmth or tone
K,L,M - Noticeable color
N to Z - Easily Noticeable color

Carat Weight
Carat is specifically a measure of a diamond's weight A one-carat diamond is comprised of 100 points called cents . Hence, 50 cents is equal to 1/2-carat, and so on.
Most of the time ,value of the diamond increases with increase in Carat size.
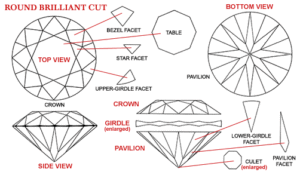
Cut
Cut is a diamond's most important characteristic. It has the greatest overall influence on a diamond's beauty. It determines what we generally think of as sparkle.
A diamond's cut grade is an objective measure of a diamond's light performance, or, what we generally think of as sparkle. When a diamond is cut with the proper proportions, light is reflected back to the top of the diamond. If it is cut too shallow, light leaks out of the bottom; too deep and it escapes out of the side.
EX - Excellent: Reflects nearly all light that enters the diamond. An exquisite and rare cut. All the dimensions are perfectly maintained in the described mathematical proportions in order to get the most sparkle.
VG - Very good cut: Reflects almost the same light as an Excellent cut, with slightly broader proportions.
GD - Good cut: Reflects most light that enters. In this case , cutter might have chosen to get bigger size to make it more economical.
FR - Fair cut: Reflects lower proportion of light due to weaker proportion that cutter has chosen to get maximum size or yield . These cuts are heavily discounted in price.
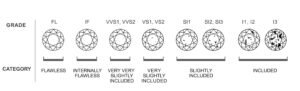
Clarity
Clarity is a measure of the number and size of the tinyimperfections that occur in almost all diamonds.
Many of these imperfections are microscopic, and do notaffect a diamonds beauty in any discernible way.
Clarity simply refers to the tiny, natural imperfectionsthat occur in all but the finest diamonds. Gemologists refer to theseimperfections by a variety of technical names, including blemishes andinclusions, among others.
Diamonds with the least and smallest imperfectionsreceive the highest clarity grades. Because these imperfections tend to bemicroscopic, they do not generally affect a diamonds beauty in any discernibleway.
"eye-clean" diamond is the one that has noimperfections visible to the unaided-eye through the face-up.
FL,IF - Flawless, Internally Flawless: No internal or external imperfections. Internally Flawless: No internal imperfections. Very rare.
VVS1,VVS2 - Very, Very Slightly Included: Very difficult to see imperfections under 10x magnification. An excellent quality diamond.
VS1,VS2 - Very Slightly Included: Imperfections are not typically visible to the unaided eye. Less expensive than the VVS1 or VVS2 grades.
SI1,SI2 - Slightly Included: Imperfections are visible under 10x magnification, and may be visible with the unaided eye.
I1 - Included: This grade of diamonds will have minor inclusions that may be visible to the unaided eye.
I2,I3 - Inclusions are heavy and visible to the unaided eye.
Know About Gemstone
Gemstones are naturally occurring, mineral crystals that are valued for their beauty, durability, and rarity, often used in jewelry. They are typically cut and polished to enhance their luster and color. Gemstones can be broadly classified as precious or semi-precious, with precious stones like diamonds, rubies, sapphires, and emeralds being highly valued for their rarity and exceptional qualities.
Here's a more detailed look:
What are Gemstones?
Definition:
A gemstone is a mineral crystal that is cut and polished to be used for jewelry or other adornments.
Origin:
Gemstones are naturally formed in the earth's crust, often through the cooling of mineral-rich hydrothermal water or as a result of rock transformations.
Categories:
Precious Stones: Diamonds, rubies, sapphires, and emeralds are the four traditionally recognized precious gemstones.
Semi-Precious Stones: This category includes a wide variety of gemstones, such as amethyst, garnet, opal, tourmaline, and many others.
Factors that Determine Gemstone Value:
Rarity: Gemstones that are less common are generally more valuable.
Beauty: A gemstone's color, clarity, and cut all contribute to its visual appeal and value.
Durability: The hardness and resistance of a gemstone to scratching and wear affect its suitability for jewelry and, consequently, its value.
Common Gemstones and Their Characteristics:
Diamond: Known for its hardness, brilliance, and clarity.
Ruby: A red gemstone, a variety of corundum, prized for its deep color.
Sapphire: A blue gemstone, also a variety of corundum, valued for its durability and color.
Emerald: A green gemstone, a variety of beryl, prized for its rich color and transparency.
Amethyst: A purple gemstone, a variety of quartz, known for its beauty and affordability.
Opal: Known for its unique play-of-color and water-like appearance.
Pearl: An organic gemstone, produced by mollusks, known for its smooth surface and pearly luster.

Yellow Sapphire - Pukhraj
Species: Corundum
Hardness: 9
Refractive Index (RI) : 1.762~1.770
Color: Light to Dark Yellow, Pale - Yellow,
Orangish Golden - Yellow
Occurrence: Sri Lanka, Burma, Thailand, Cambodia, Africa, Australia.

Blue Sapphire - Neelam
Species: Corundum
Hardness: 9
Refractive Index (RI) : 1.762~1.770
Color: Light to Dark Blue, Violetish - Blue, Greenish - Blue, Purplish - Blue
Occurrence: Kashmir, Burma, Thailand, Pakistan, Vietnam, Sri Lanka, Africa, Australia.

Ruby - Manaik
Species: Corundum
Hardness: 9
Refractive Index (RI): 1.762~1.770
Color: Light to Dark Red, pinkish/Purplish Red
Occurrence: Burma, Thailand, Pakistan, Vietnam, Sri Lanka, Africa.

Emerald - Panna
Species: Chrysoberyl
Hardness: 7.5-8
Refractive Index (RI): 1.577~1.583
Color: Light to Dark Green.
Occurrence: Colombia, Brazil, Russia, Zambia, India.

Pearl - Moti
Species: Fresh Water, Salt Water
Hardness: Varies
Refractive Index (RI): Not Applicable (Opaque)
Color: White, Grey, Yellowish - White, Light - Cream, Black, Body - Color
Occurrence: Seas of Basra, South Sea, Tahiti, Arabia, Australia, Japan, Bahrain, Persia.

Hessonite - Gomed
Species: Grossularite
Hardness: 7 - 7.5
Refractive Idex (RI): 1.740
Color: Brown, Brownish - Orange, Orangish - Brown.
Occurrence: Sri Lanka, Canada, Canada, Brazil. Africa, Madagascar.

Red Coral - Lal Moonga
Species: Corundum
Hardness: 3.5 - 4.0
Refractive Index (RI) : Not Applicable as they are Opaque
Color: Flesh Pink, Dark Blood Red, Orange, Orangish - Red, Brownish - Red
Occurrence: Mediterranean Sea, Red Sea, Sea near Spain, Morocco, Malaysia, Japan.

Diamond - Hira
Species: Carbon
Hardness: 10
Refractive Index (RI): 2.417
Color: Colorless, Yellow, Brown, Red, Green, blue, other Fancy Colors
Occurrence: Africa, Russia, Canada, Australia, India.

